Bookkeeping
Operating Income Meaning, Formula, & Its Difference to Others
Content
Therefore, the determination of each quarter’s material needs is partially dependent on the following quarter’s production requirements. The desired ending inventory of material is readily determined for quarters 1 through 3 as those needs are based on the production requirements for quarters 2 through 4. To compute the desired ending materials inventory for quarter 4, we need the production requirements for quarter 1 of year 2.
In quarter 4, Leed Company plans income taxes of $142,500 to be paid in the first quarter of the following year making this the ending balance for Income Taxes Payable. EBIT refers to Earnings Before Interest and Taxes and can be calculated by taking total revenue less the cost of goods sold and the regular selling, general, and administrative costs (SG&A). Sometimes EBIT is presented directly on the income statement, but it is not a requirement of US GAAP to directly report. Given the direct labor hours for each quarter from the direct labor budget, the variable costs are the number of hours multiplied by the variable overhead application rate.
What are earnings before interest and taxes?
Non-operating IncomeNon-Operating Income, also called Peripheral Income, is the capital amount that a business earns from non-core revenue-generating activities. The examples include profits/losses from a capital asset sale or Foreign Exchange Transactions, Dividend Income, Lawsuits losses, & Asset Impairment losses, etc. Operating RevenueOperating revenue is defined as revenue earned by an individual, corporation, or organization from the core activities that they undertake on a regular basis. There are several methods to earn revenue, but operational revenue is earned by the core business activities that the organization undertakes in its daily operations. To meet production or sales targets, both short-term and long-term financial estimates are sometimes evaluated. When creating your income statement, you can decide how to classify your expenses.
Examples of expenses included under operating income include manufacturing costs, employee wages, advertising fees and administrative expenses. Last, the company is reporting a very material increase in provision for income taxes as Apple, Inc. estimated an additional $1 billion of expenses from what had been incurred one year ago. First, the company’s cost of goods sold increased from last year to this year. Both “Research and Development” as well as “Selling, General, and Administrative” expenses increased. The company spent $11.129 billion on operating expenses the year prior; now, it had reported operating expenses of almost $13 billion. If a company does not have interest expenses, tax expenses, or other non-operational costs, it is possible for a company’s operating income to be the same as its net income.
Fixed costs
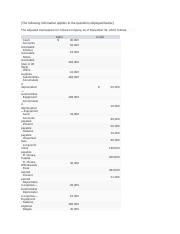
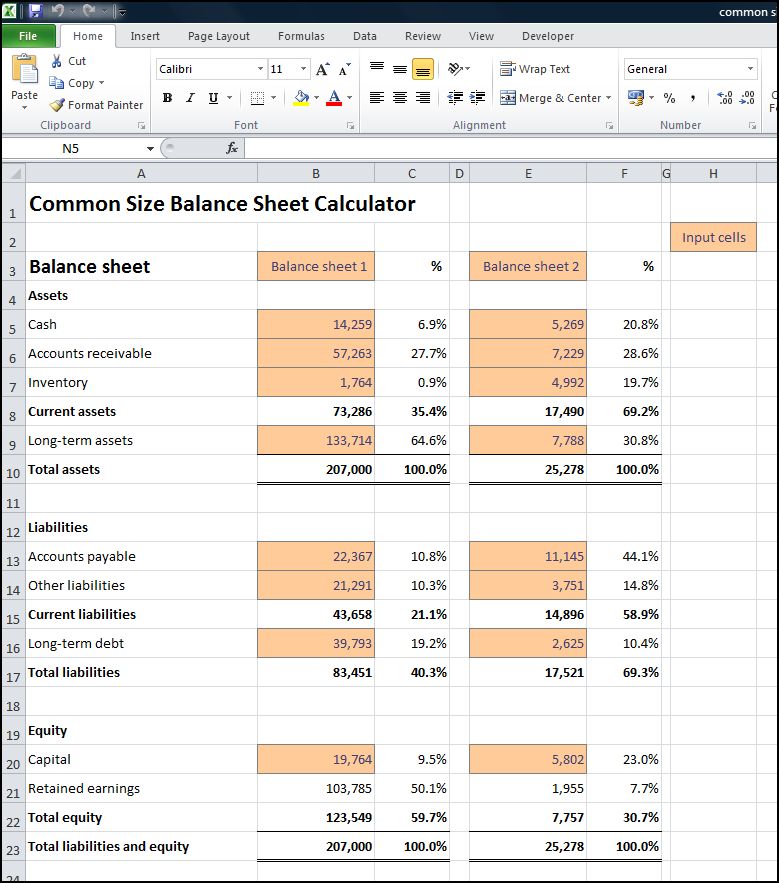
Beginning retained earnings comes from the balance of last year’s balance sheet of $400,000. Net Income comes from the budgeted income statement for the year of $855,000. Dividends can be determined from the schedule of cash payments which shows $120,000 paid this year. For Leed Company, there were no changes to the Land account so the balance will remain at $60,000. Leed purchased a new building for $650,000 in the 4th quarter so the new building balance is $1,650,000 ($1,000,000 last year + 650,000 new building). According to the manufacturing overhead budget, we planned $40,000 of factory equipment depreciation this year.
EPS largely depends on the company’s earnings, which requires EBIT to shed light on the amount of profit that remains after accounting for necessary expenses. EBITDA can offer a more accurate impression of a company’s operating profit than EBIT, especially for companies with a substantial number of fixed assets. To calculate EBIT, you should deduct direct and indirect expenses from the net revenue, excluding interest and tax. Finally, the interest payments and taxes are subtracted from the remaining number. In other words, net income is the amount of profit the company expects to earn during the predetermined period. This is the total amount of revenue that the company expects to bring in from its sales.
Resources created by teachers for teachers
Often regarded as the cost of goods sold or cost of sales, the expenses are specifically related to the cost of producing goods or services. The costs can be fixed or variable but are dependent on the quantity being produced and sold. On the other hand, gross profit is the monetary result obtained after deducting the budgeted operating income formula cost of goods sold and sales returns/allowances from total sales revenue. Begin putting together your operating budget by, collaboratively with other managers, agreeing upon a revenue estimation. Then, have input from managing staff to estimate expenses for the coming year required to meet this projected revenue.
Stockholder’s Equity is comprised of common stock and retained earnings. Retained Earnings is the earnings of the company over time minus any dividends paid. Accounts Payable is determined using the purchases budget and the schedule of cash payments. The balance in Accounts Receivable represents credit sales that have not been collected during the year.
Determine variable costs
Management must consider the effects of planned activities on these balances. Many accounts are affected by items in the planned operating budget, by cash inflows and outflows, and by policy decisions. Management uses the planned operating budgets and cash budget to prepare the project balance sheet for this year.
- Operating income is a measurement that shows how much of a company’s revenue will eventually become profits considering its business operations.
- Investors monitor operating income as it gives an idea of the future scalability of the company.
- Meanwhile, a negative operating profit could mean the business is less likely to scale up and grow.
- It includes five different example spreadsheets with varying levels of specificity.
- It’s important to note that operating income is different than net income.
Since 6,000 units are sold, $112,200 (6,000 units × $18.70 per unit) will be expensed as cost of goods sold, while the remaining $19,663 will be part of finished goods ending inventory. The sales budget leads into the production budget to determine how many units must be produced each week, month, quarter, or year. It also leads into the cash receipts budget, which will be discussed in10.3 Financial Budgets.



Bài viết liên quan: